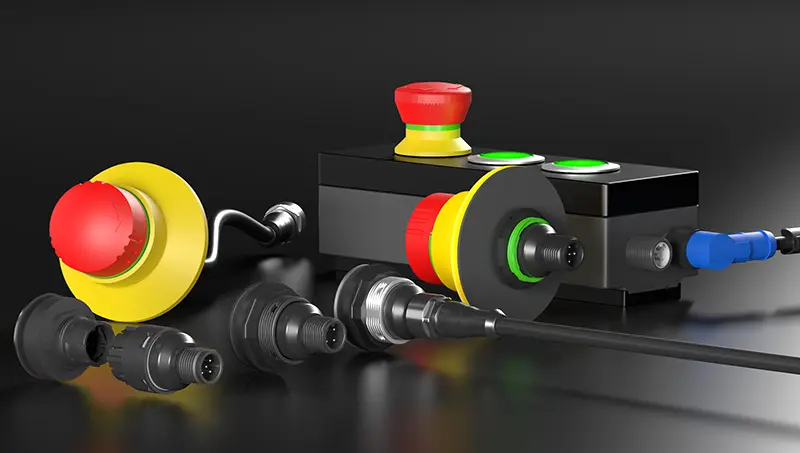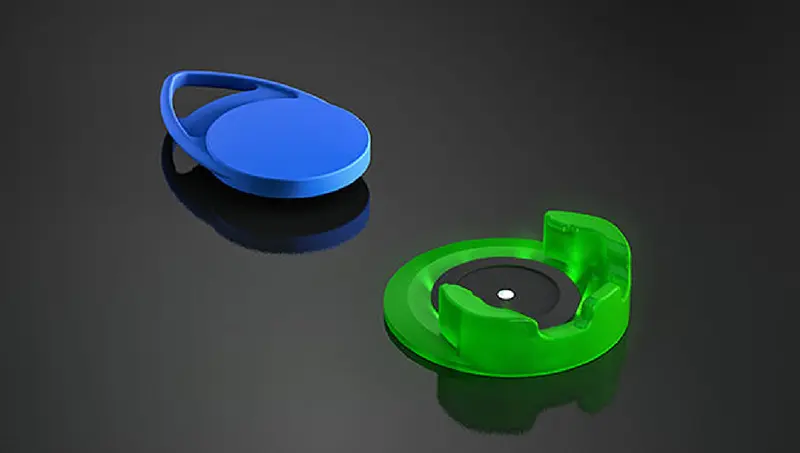

Schlegel offers three RFID Systems
For customised applications
RFID-Standard - for individual, special requirements (freely configurable)
RFID SKS - for quick and easy integration in areas with few requirements (up to 25 transponders)
RFID TMS - for flexible application in areas with complex requirements (various number of transponders possible)
Depending on the version, the RFID systems support the following operating modes:
Cyclic and/or single reading
FAQ
What is RFID?
RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification and describes the contactless identification of objects via radio waves. An RFID system always consists of a reading unit and one or more transponders (so-called tag).
How does the setup of an RFID system look like?
The transponder consists of a coil (antenna) and a microchip that carries the data. The reading device generates an electromagnetic field via radio waves. If there is a transponder present within this field, its coil induces electricity and creates a signal, which the reading device can receive and analyse.
How are RFID systems used?
A typical field of application for RFID is the identification of people, e.g. access controls or time recordings. But also identification of objects, e.g. in relation to authenticity checks, maintenance or production, is often realised by using RFID.
Which RFID technologies are there?
RFID is available for various frequencies. To put it simple, the longer the required range, the more energy is needed. There is a distinction between three frequency ranges: LF (low) covers areas of < 135 KHz and < 0.1 m, HF (high) covers areas of 13.56 MHz and < 0.5 m, UHF (ultra high) covers areas of 865 – 928 MHz and < 10 m.





